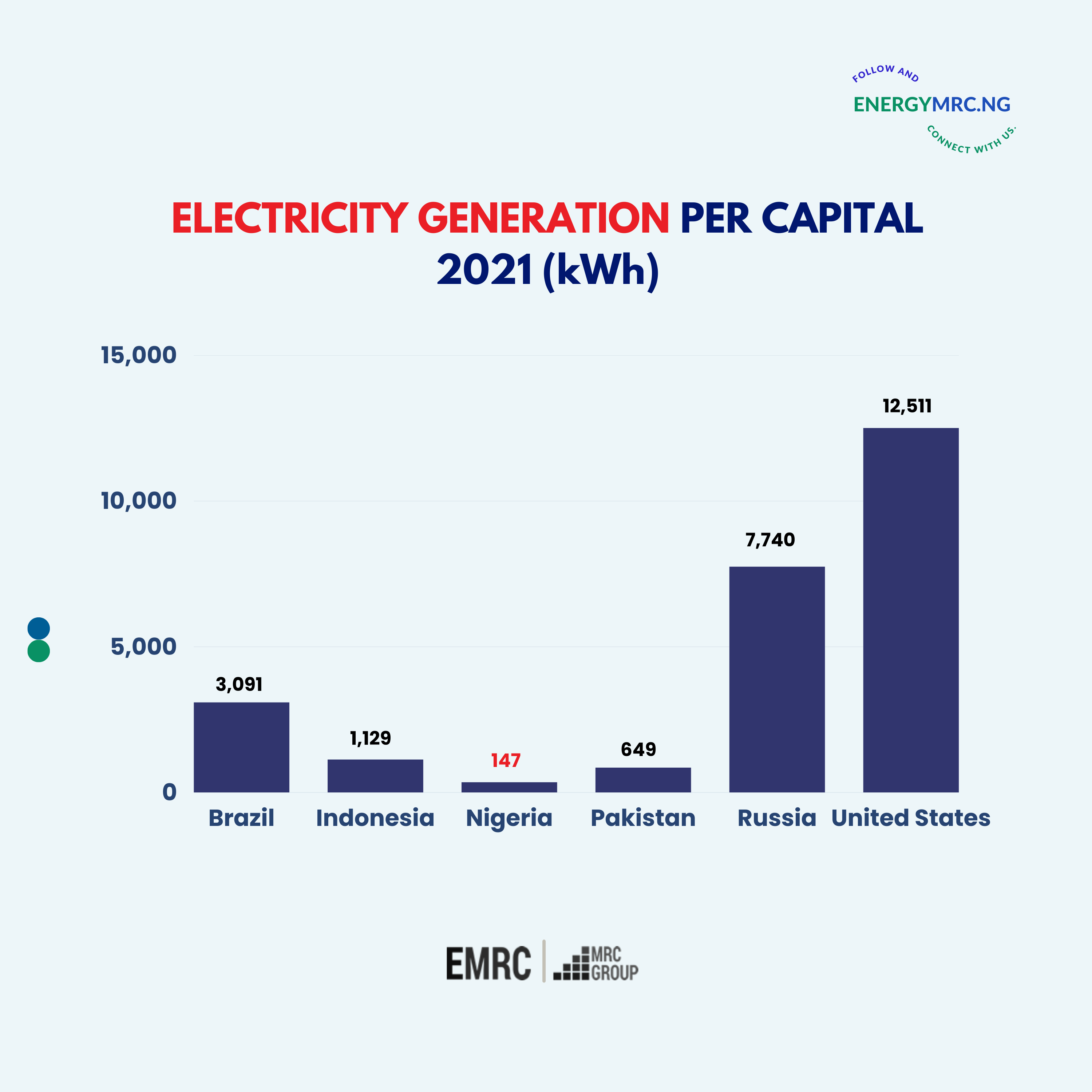
Energy access is a crucial part of the development and progress of any country today. One of the most important metrics used to measure this is the electricity generation per capita, which measures the average annual electricity generation per person in a given area, expressed in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
Developed countries typically have high rates, usually 1500 kWh or higher, indicating greater energy access. Developing countries, on the other hand, have lower generation per capita rates, with Nigeria's rate of 147 kWh being quite low, especially for a country with its population size and economic potential. In comparison, similarly sized developing countries such as Brazil and Pakistan have higher per capita rates and developed countries with similar populations as Nigeria, such as the United States and Russia, have rates far above 5000 kWh.
Evidently, there is a need to improve electricity access across the country. To achieve this, Nigeria must support the upgrade of the existing energy infrastructures in the country; power plants, transmission lines, and distribution networks. This will improve the efficiency and reliability of the power supply.